The Call Stack defined on MDN
A call stack is a mechanism for an interpreter (like the JavaScript interpreter in a web browser) to keep track of its place in a script that calls multiple functions — what function is currently being run and what functions are called from within that function, etc.
- When a script calls a function, the interpreter adds it to the call stack and then starts carrying out the function.
- Any functions that are called by that function are added to the call stack further up, and run where their calls are reached.
- When the current function is finished, the interpreter takes it off the stack and resumes execution where it left off in the last code listing.
- If the stack takes up more space than it had assigned to it, it results in a “stack overflow” error.
Example
function greeting() { // [1] Some code here sayHi(); // [2] Some code here } function sayHi() { return “Hi!”; }
// Invoke the greeting function
greeting();
// [3] Some code here
explanation
- When the greeting() function is invocated. It is added to the call stack list.
- The code inside the greeting() function is executed.
- The sayHi() function is invocated.
- The sayHi() function is added to the call stack list.
- The code inside the sayHi() function is executed.
- The sayHi() and continue executing the rest of the greeting() function.
- The sayHi() function is deleted from our call stack list
- When everything inside the greeting() function has been executed, return to its invoking line to continue executing the rest of the JS code.
- The greeting() function is deleted from the call stack list.
- The call stack list is now empty.
Understanding the JavaScript Call Stack
Essentially, a call stack is a data structure that uses the Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle to temporarily store and manage function invocation (call).
JavaScript error messages
What causes a stack overflow?
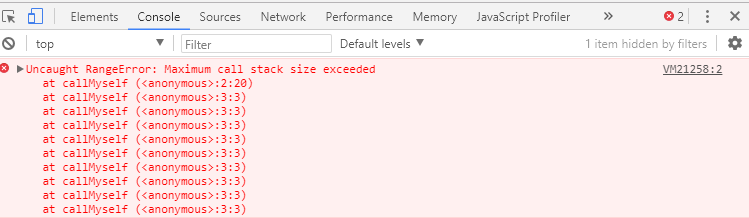
A stack overflow occurs when there is a recursive function (a function that calls itself) without an exit point. The browser (hosting environment) has a maximum stack call that it can accomodate before throwing a stack error. Hwer’s aan example of a stack overflow.
This code will run until the browser gives an error:
function callMyself(){ callMyself(); } callMyself();
References
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/Call_stack
- https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/understanding-the-javascript-call-stack-861e41ae61d4/
- https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/understanding-the-javascript-call-stack-861e41ae61d4/